Useful sample Python Scripts
TIS 6.0 samples
Project file: Python Samples.gzip
Input data structure
Script file: input.py
By convention the first 2 rows define the types and captions of the input columns.
def main(params,inputs,outputs): columns = {} types = {} async def donothing(): # receives each row in v and sends it unmodified nonlocal columns v = None while 1: v = yield v i0 = inputs[0] o0 = outputs[0] return [ (i0, donothing(), o0) ], {i0: (lambda: (types, columns))} Refer to columns by caption
Use nonlocal to refer to variables in the main method's scope in order to be available in another nested method, such as inc in this sample.
Note: gen.__anext__() will be replaced by anext(gen) in Version 3.7, see https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0525/#aiter-and-anext-builtins
# one input, one output# duplicate input rows with row idsdef main(params,inputs,outputs): Birthday = None columns = {} types = {} async def getcolfilter(i): nonlocal Birthday nonlocal columns Birthday = columns['Birthday'] async for v in i: yield v async def inc(): nonlocal Birthday v = None while 1: v = yield v # produce v, then wait for next v v[Birthday] += datetime.timedelta(days=365) i0 = inputs[0] o0 = outputs[0] return [ (getcolfilter(i0), inc(), o0) ], {i0: (lambda: (types, columns))} Aggregate input into a list
Each yield internally calls asend then waits with anext.
Prime
Every generator must be initialized with a None, otherwise, following exception occurs:
await o.asend(v) File "user_script.py", line 18, in flush TypeError: can't send non-None value to a just-started async generator
# aggregates complete input into a list # flushes list to output def main(params, inputs, outputs): async def sponge(i): mylist = [] async for v in i: mylist.append(v) yield mylist async def flush(o): mylist = yield await o.asend(None) # prime o ----> Note: For TIS version 6.2 or higher remove this statement !!! for v in mylist: await o.asend(v) i0 = inputs[0] o0 = outputs[0] return [ (sponge(i0), flush(o0)) ]Add a new column to output
Input has a date column named "Birthday".
An output row v is a list, so appending creates an additional column.
# input has a date column named 'Birthday'# add a new column 'age' to outputdef main(params,inputs,outputs): from datetime import date columns = {} types = {} async def addage(): nonlocal columns, types types[len(columns)] = int columns['Age'] = len(columns) v = None while 1: v = yield v a = age(v[columns['Birthday']]) v.append(a) def age(birthday): today = date.today() age = (today.year - birthday.year - \ ((today.month, today.day) < (birthday.month, birthday.day))) return age i0 = inputs[0] o0 = outputs[0] return [ (i0, addage(), o0) ], {i0:(lambda: (types,columns)), o0:(lambda: (types,columns))}Delete columns to output
An output row v is a list, so deleting some columns.
# delete columns ... to outputdef main(params,inputs,outputs): from datetime import date columns = {} types = {} def delcolumns(names): new_columns = {} new_types = {} i = 0 for column in columns.keys(): if not column in names: new_columns[column] = i new_types[i] = types[columns[column]] i += 1 columns.clear() types.clear() columns.update(new_columns) types.update(new_types) async def delete_specified_columns(): nonlocal columns, types, params delete_columns = ['col1','col2'] deleted_indices = [] for column in delete_columns: deleted_indices.append(columns[column]) delcolumns(delete_columns) print('deleted column indices : ', deleted_indices) v = None while 1: v = yield v #print(v) row = v[:] v.clear() #print(row) for i, column in enumerate(row): if not i in deleted_indices: v.append(column) i0 = inputs[0] o0 = outputs[0] return [ (i0, delete_specified_columns(), o0) ], {i0:(lambda: (types,columns)), o0:(lambda: (types,columns))}Using WebAPI
This sample shows some parts for using a REST-ful WebAPI.
- wrapper class for the WebAPI
- wrapper class and method for simple_main (that is part of the framework starting from version 6.0)
- a simple_main routine defining the output schema and data
import datetimeimport requestsimport json## wrapper class for some web-api using HTTP Basic Auth#class someapi: # # initializes the object and keeps the credentials auth is tuple of (username,password) # def __init__(self, auth): self.api_url_base = 'https://host/service/api/1/' self.api_auth = auth # # this api requires a session # def getsession(self): api_url = self.api_url_base + 'session' response = requests.get(api_url, auth=self.api_auth) if response.status_code == 200: content = json.loads(response.content.decode('utf-8')) self.sessionid = content['id'] return content return [] # # some method for retrieving # def getthings(self): api_url = self.api_url_base + 'something' response = requests.get(api_url, headers = {'sessionid' : self.sessionid}) if response.status_code == 200: content = json.loads(response.content.decode('utf-8')) return content return [] # # get details of a specified thing # def getdetails(self, id): api_url = self.api_url_base + 'something/' + id + '/details' response = requests.get(api_url, headers = {'sessionid' : self.sessionid}) if response.status_code == 200: content = json.loads(response.content.decode('utf-8')) return content return []## wrapper class for simple_main# class SimpleMain: """Wrapper for simple_main(params, sponge_list, types, columns).""" types = {} columns = {} def __init__(self, user_script, params, inp): self.user_script = user_script self.params = params self.inp = inp async def sponge(self): """Async generator that yields results from user_script.""" for res in self.user_script(self.params, [row async for row in self.inp], self.types, self.columns): yield res def get_types_columns(self): """Return pair of types and columns.""" return self.types, self.columns## actual main routine#def simple_main(params, mylist, types, columns): def addcolumn(name, type): columns.update({name:len(columns)}) types.update({len(types):type}) # output list out_list = [] # specify output schema addcolumn('Thing', str) addcolumn('ThingId', str) # get credentials from parameters auth = (params['api_auth_username'],params['api_auth_password']) # use wrapper class for api w = someapi(auth) session = w.getsession() things = w.getthings() # fill in output list for row in mylist: for thing in things: out_list.append(tuple(row) + (thing['name'], thing['id'])) return out_list ## wrapper function for simple_main# def main(params, inputs, outputs): inp, out = inputs[0], outputs[0] simple = SimpleMain(simple_main, params, inp) return [(simple.sponge(), out)], { inp: simple.get_types_columns, out: simple.get_types_columns }Accept self-signed SSL certificates using pytisapi
From TIS 6.2 onwards:
The TISEditorApi constructors accepts a verify parameter, which defaults to True. For working with self-signed certificates, set this parameter to False when initializing the object.
import pytisapitisEditor = pytisapi.TISEditorApi(verify=False)Prior to TIS 6.2:
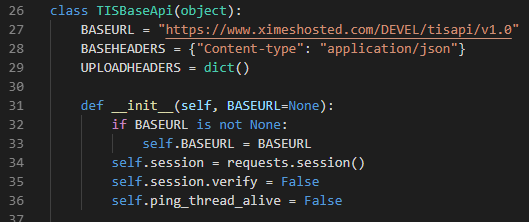
Patch Python\pytisapi\baseapi.py
include self.session.verify = False in line 34
Disable Warnings in your script
import urllib3urllib3.disable_warnings()For older versions urllib3 was embedded into requests see also https://stackoverflow.com/questions/27981545/suppress-insecurerequestwarning-unverified-https-request-is-being-made-in-pytho
import requestsfrom requests.packages.urllib3.exceptions import InsecureRequestWarningrequests.packages.urllib3.disable_warnings(InsecureRequestWarning)TIS 6.2 samples
Project file: Python_Samples_V6.2.zip
Asynchronous CSV import
This sample shows how to import a CSV file using the async version of the create_table function. Input file: cities.csv
async def create_table(parameters, types, columns, files): is_first = True textreader = files.i[0].textreader(newline='\n') async for l in textreader: if is_first: headers = [v.strip(' "\n') for v in l.split(',')] for col_idx, h in enumerate(headers): columns[h] = col_idx is_first = False else: fields = [v.strip(' "\n') for v in l.split(',')] if [ f for f in fields if f ]: yield fieldsDefine data node start table schema
This sample shows how to define a data node start table schema using the create_table function.
def create_table(params, types, columns, files): types[0] = int types[1] = str types[2] = datetime.datetime types[3] = float types[4] = bool columns['Integer Column'] = 0 columns['String Column'] = 1 columns['DateTime Column'] = 2 columns['Float Column'] = 3 columns['Boolean Column'] = 4 return []Create table with random test data
This sample shows how to create a data table with random test data using the async version of the create_table function.
import randomimport uuidasync def create_table(params, types, columns, files): types[0] = int types[1] = str types[2] = int columns['ID'] = 0 columns['Random string'] = 1 columns['Random integer'] = 2 n = 10000 for i in range(n): yield [ i, uuid.uuid4(), random.randint(0, 1000) ]Simple main for data export
This sample shows how to export data using the async version of the simple_main function.
async def simple_main(params, input, types, columns, files): textwriter = files.o[0].textwriter() col_exp_cnt = len(columns) i = 0 textwriter.write('\t'.join(['"' + c + '"' for c in columns.keys()]) + '\r\n') async for v in input: await textwriter.write_async('\t'.join(['"' + c + '"' if isinstance(c, str) else str(c) for c in v]) + '\r\n') i += 1 types[0] = bool types[1] = int types[2] = int columns['Export status'] = 0 columns['Column export count'] = 1 columns['Row export count'] = 2 yield [True, col_exp_cnt, i]Simple main using bytewriter
This sample shows how to export data using the async version of the simple_main function.
async def simple_main(params, input, types, columns, files): bytewriter = files.o[0].bytewriter() async for v in input: text = '\t'.join([str(c) for c in v]) + '\r\n' await bytewriter.write_async(text.encode()) types[0] = bool columns['Export result'] = 0 yield [ True ]Create table reading Japanese character
This sample shows how to read a file containing a Japanese character one character at a time using the create_table function. Input file: japanese_char.txt
def create_table(params, types, columns, files): textreader = files.i[0].textreader() while True: c = textreader.read(1) if c == '': break yield [c]Using pytisapi for recalculating data nodes
This sample shows how to use pytisapi in current session for recalculating data nodes of specified projects
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# result table## Project | Datanode | StartTime| EndTime | Status def create_table(params, types, columns, files): def addcolumn(name, type): columns.update({name:len(columns)}) types.update({len(types):type}) # specify output schema addcolumn('Project', str) addcolumn('Datanode', str) addcolumn('StartTime', str) #datetime.datetime) addcolumn('EndTime', str) #datetime.datetime) addcolumn('Status', str) # pytisapi import pytisapi from pytisapi.editormapper.editor import Editor result = [] try: with Editor.from_token(baseurl=kwargs['sessionUrl'], token=kwargs['sessionToken']) as editor: projects = editor.get_projects() # --- iteration 1 project_name ='Project A' dn_name = 'A00 Data node' project = projects[project_name] dns = project.get_datanodes() dn = dns[dn_name] task_id = dn.recalculate() # 720 sec waiting time _, resp = editor.api.get_task(task_id) print(resp) result.append([project_name, dn_name, resp['StartTime'], resp['EndTime'], resp['Status']]) # --- except pytisapi.TISApiException as e: print("failed with %r" % (e)) return return result Using pytisapi for renaming data nodes
This sample shows how to use pytisapi in current session for renaming data nodes of specified projects
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# input table## Project# result table## Project | Folder | Datanode | Datanode_new | Actiondef main(params,inputs,outputs, **kwargs): # Regular expressions import re # pytisapi import pytisapi from pytisapi.editormapper.editor import Editor # input table data structure columns = {} types = {} def get_folder_prefix(folder): x1 = re.findall("^([^\s]+)", folder) x2 = re.findall("^[^_]+(?=_)", folder) if not x1: x = x2[0] elif not x2: x = x1[0] else: if len(x1[0]) > len(x2[0]): x = x2[0] else: x = x1[0] # cuts foldername longer than 5 character if len(x) > 5: x = x[:5] return x async def rename(project, dns, folder_node, o): # position of data node in folder y = 1 for child in folder_node.get_children_list(): if child.is_datanode(): datanode = dns[child.attrs['Caption']] folder = folder_node.attrs['Caption'] folder_prefix = get_folder_prefix(folder) datanode_name_cutted = re.sub(r"(?:\w+\s)(.*)", r"\1", datanode.attrs['Caption']) datanode_name_new = folder_prefix + '_' + str(y).zfill(2) + " " + datanode_name_cutted trancated = False if len(datanode_name_new) > 50: datanode_name_new = datanode_name_new[:50] trancated = True v = [project.attrs['Caption'], folder, datanode.attrs['Caption']] if datanode.attrs['Fixed']: v.append(None) v.append('Ignored because data node is Fixed') elif datanode.attrs['Caption'] == datanode_name_new: v.append(None) v.append('OK') else: #updates the project with the new names child.rename(datanode_name_new) v.append(datanode_name_new) if trancated: v.append('Renamed and trancated') else: v.append('Renamed') await o.asend(v) y += 1 else: await rename(project, dns, child, o) async def sponge(i): mylist = [] async for v in i: mylist.append(v) yield mylist async def flush(o): nonlocal columns, types input_table = yield # add columns to result table types[len(columns)] = str columns['Folder'] = len(columns) types[len(columns)] = str columns['Datanode'] = len(columns) types[len(columns)] = str columns['Datanode_new'] = len(columns) types[len(columns)] = str columns['Action'] = len(columns) try: with Editor.from_token(baseurl=kwargs['sessionUrl'], token=kwargs['sessionToken']) as editor: projects = editor.get_projects() for input_row in input_table: project = projects[input_row[columns['Project']]] tree = project.get_projecttree() datanodes = project.get_datanodes() await rename(project, datanodes, tree, o) except pytisapi.TISApiException as e: print("failed with %r" % (e)) return i0 = inputs[0] o0 = outputs[0] # pipeline return [ (sponge(i0), flush(o0)) ], {i0:(lambda: (types,columns)), o0:(lambda: (types,columns))}Generate a CSV file from input table and attach to PDF file
This sample shows how to attach a data file in CSV format to a PDF file
import fitzimport datetimeimport osimport csvimport io# Requirements:# pymupdf ## Input-Parameters:# PDF_Path ....... absolute path to file on server file system# PDF_Filename ... PDF filename## Input-Table:# all rows and column headers are written to CSV file and attached to specified PDF file#def simple_main(params, mylist, types, columns): filepath = os.path.join(params["PDF_Path"], params["PDF_Filename"]) downloadpath = "../../TISResults/Pdf/" + params["PDF_Filename"] # generate csv file in memory attachment_filename = "attachment.csv" output = io.StringIO() writer = csv.writer(output, dialect='excel') writer.writerow(columns.keys()) writer.writerows(mylist) attachment_content = bytearray(output.getvalue(), "utf-8-sig") # attach file to pdf doc = fitz.open(filepath) if attachment_filename in doc.embeddedFileNames(): doc.embeddedFileDel(attachment_filename) doc.embeddedFileAdd(attachment_filename, attachment_content) doc.saveIncr() # generate downlink html types.clear() columns.clear() types[0] = str columns['Result'] = 0 return [["""<a href="%s" target="_blank">PDF Bericht herunterladen</a>""" % (downloadpath)],]Save table i1 and iterate table i0
import datetimeimport randomdef main(params, inputs, outputs): types_t0 = {} columns_t0 = {} types_t1 = {} columns_t1 = {} i0 = inputs[0] i1 = inputs[1] o0 = outputs[0] types_o0 = {0: str, 1: str } columns_o0 = {'Beginn': 0, 'Dauer': 1, } # Ändert Zeile für Zeile async def simulate(): # Hier speichern wir die gesamte Tabelle aus i1 historic_data = [] async for row in i1: historic_data.append(row) print(len(historic_data)) # Wir machen hier eine Endlosschleife, weil wir erst aufhören möchten zu warten, # wenn explizit geschlossen wird (darum kümmert sich der pymeta) # Wir initialisieren die zu verschickende Zeile mit None new_row = None while True: # Wir senden eine Zeile und holen uns danach eine neue # (senden passiert vor empfangen) # (In der ersten Iteration wird None verschickt) row = yield new_row # Wir bauen die als nächste zu verschickende Zeile new_row = [row[1], row[2]] # Der Workflow schiebt Zeilen aus i0 in simulate() und Zeilen aus simulate() weiter in o0 workflow_defs = [ (i0, simulate(), o0) ] schema_defs = { i1: (lambda: (types_t1, columns_t1)), i0: (lambda: (types_t0, columns_t0)), o0: (lambda: (types_o0, columns_o0)), } return workflow_defs, schema_defsSponge multiple input tables
import datetimeimport randomdef main(params, inputs, outputs): types_t0 = {} columns_t0 = {} types_t1 = {} columns_t1 = {} types_t2 = {} columns_t2 = {} types_t3 = {} columns_t3 = {} i0 = inputs[0] i1 = inputs[1] i2 = inputs[2] i3 = inputs[3] o0 = outputs[0] types_o0 = {0: str, 1: str } columns_o0 = {'Beginn': 0, 'Dauer': 1, } async def sponge(i): mylist = [] async for v in i: mylist.append(v) dn1 = [] async for row in i1: dn1.append(row) dn2 = [] async for row in i2: dn2.append(row) dn3 = [] async for row in i3: dn3.append(row) print("dn1: ", len(dn1)) print("dn2: ", len(dn2)) print("dn3: ", len(dn3)) # do something here yield mylist async def flush(o): mylist = yield for v in mylist: await o.asend(v) workflow_defs = [ (sponge(i0), flush(o0)) ] schema_defs = { i3: (lambda: (types_t3, columns_t3)), i2: (lambda: (types_t2, columns_t2)), i1: (lambda: (types_t1, columns_t1)), i0: (lambda: (types_t0, columns_t0)), o0: (lambda: (types_o0, columns_o0)), } return workflow_defs, schema_defsGenerate DAO class and sample data based on input table
Used for unit testing of python-op scripts
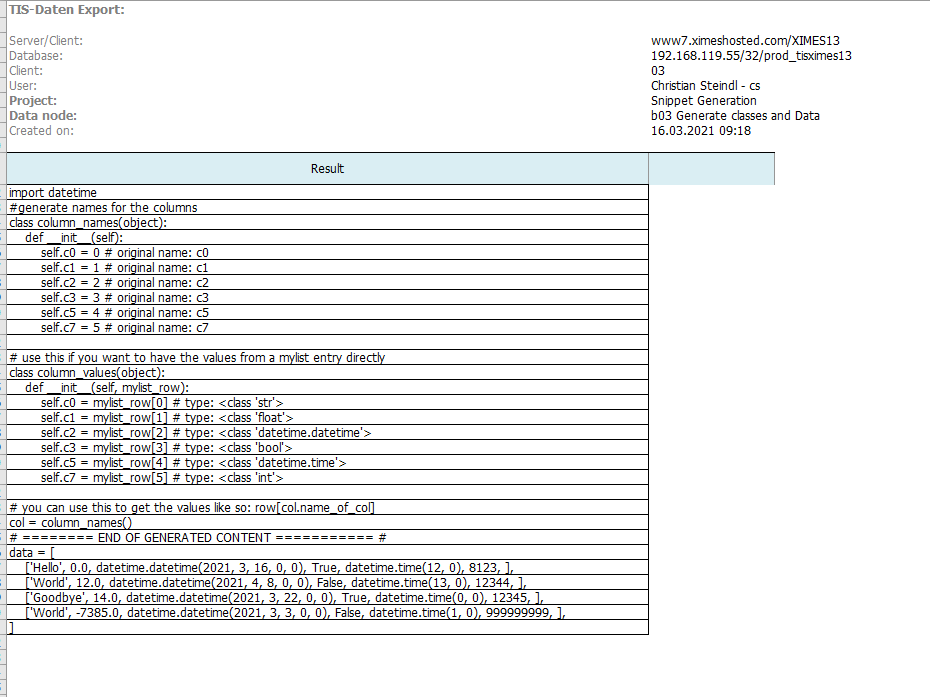
import reclass ScriptWriter(object): def __init__(self): self.lines = [] self.__indent = 0 def indent(self): self.__indent += 1 def unindent(self): self.__indent -= 1 self.__indent = max(self.__indent, 0) def line(self, text): self.lines.append((" " * self.__indent) + str(text)) def as_array(self): return self.lines def as_text(self): return "\n".join(self.lines) def convert_to_identifier(self, name): # valid python identifiers contain no spaces, no dots and do not start with numbers # we also want to replace the following characters with an underscore: prefix = "" try: n0 = name[0] int(n0) # if this works then n0 is a number prefix = "num" except: pass return prefix + self.sanitize(str(name)) @classmethod def sanitize(cls, name): """cleans the name so that it is in a format that we can work with, i.e. replaces '!,;. _-#~+*?=} {[]!§$%&/|><] with _ Args: name (str): the name to sanitize Returns: str: the sanitized name """ for c in "'!,;. _-#~+*?=} {[]!§$%&/|><]": name = name.replace(c,"_") return namedef simple_main(params, mylist, types, columns): def addcolumn(name, type): columns.update({name:len(columns)}) types.update({len(types):type}) sw = ScriptWriter() sw.line("import datetime") sw.line("#generate names for the columns") sw.line("class column_names(object):") sw.indent() sw.line("def __init__(self):") sw.indent() for ckey, cidx in columns.items(): sw.line("self." + sw.convert_to_identifier(str(ckey)) + " = " + str(cidx) + " # original name: " + str(ckey)) sw.unindent() sw.unindent() sw.line("") sw.line("# use this if you want to have the values from a mylist entry directly") sw.line("class column_values(object):") sw.indent() sw.line("def __init__(self, mylist_row):") sw.indent() for ckey, cidx in columns.items(): ident = sw.convert_to_identifier(str(ckey)) sw.line("self." + ident + " = " + "mylist_row[" + str(cidx) + "] # type: " + str(types[cidx])) sw.unindent() sw.unindent() sw.line("") sw.line("# you can use this to get the values like so: row[col.name_of_col]") sw.line("col = column_names()") sw.line("# ======== END OF GENERATED CONTENT =========== # ") out = sw.as_array() out.append("data = [") # fill in output list for row in mylist: row_str = (" " * 4) + "[" for item in row: item_repr = repr(item) if "NullType" in item_repr: item_repr = "None" row_str += item_repr + ", " row_str += "]," out.append(row_str) out.append("]") columns.clear() types.clear() addcolumn("Result", str) return outTIS 6.4 samples
Warm-up user pool
Warm-up user pool
import pytisapiimport timefrom pytisapi.editormapper.editor import Editordef create_table(params, types, columns, files): start_time = time.time() with Editor.from_token(baseurl=kwargs['sessionUrl'], token=kwargs['sessionToken'], verify=True) as editor: # add APPID of targeted TIService instances app_ids = ["1001"] username = "userpool1" task_results = [] for app_id in app_ids: # specify number of pool users as 3rd parameter _, resp = editor.userpool_warmup(username, app_id, 10) print(resp) _, task = editor.api.get_task(resp["TaskId"]) isRunning = True while isRunning: _, task = editor.api.get_task(resp["TaskId"]) isRunning = task['Status'] in ["Running", "Queued"] time.sleep(1) current_time = time.time() elapsed_time = current_time - start_time if elapsed_time * 1000 > (kwargs['timeout'] - 1000): types[0] = str columns['Result'] = 0 return task_results print(task) task_results.append([ task['Result'] ]) types[0] = str columns['Result'] = 0 return task_resultsCopy a file to several other locations (e.g. after Upload)
Copy a file to several other locations (e.g. after Upload)
def create_table(params, types, columns, files): types[0] = str columns['Result'] = 0 inreader = files.i[0].bytereader() contents = inreader.read() for ofile in files.o: bytewriter = ofile.bytewriter() bytewriter.write(contents) return [ ["Synchronized %d files" % len(files.o)] ] Erweiterterte Einstellungen - no input data - define an event afte upload to recalculate it. You can use parameters in these paths.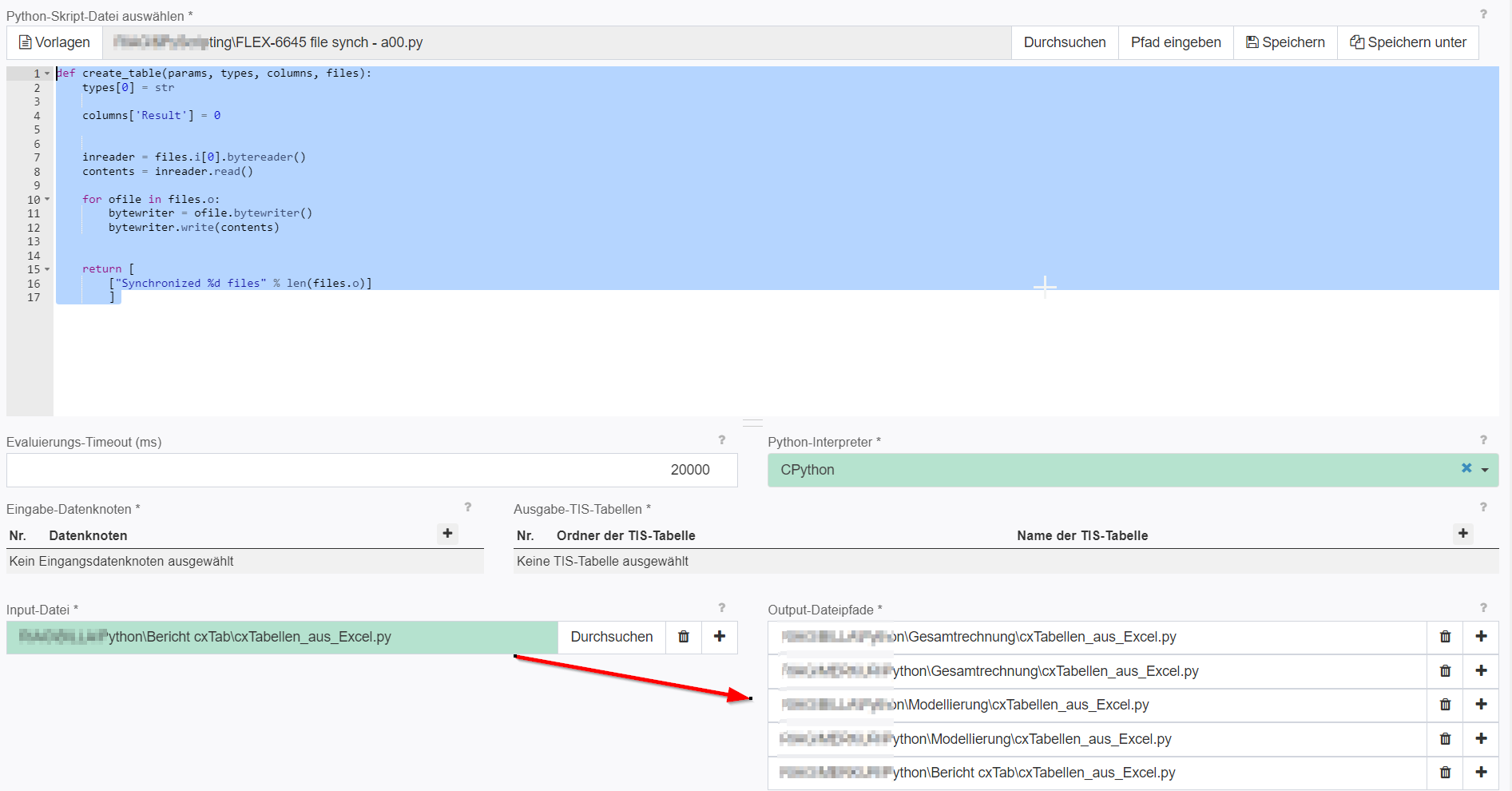
TIS 6.5 samples
TIS Board permissions
Getting and setting user permissions for TIS Board nodes
def main(params,inputs,outputs,**kwargs): from pytisapi.editormapper import Editor from pytisapi import TISApiException # Getting the Python TISApi through tiseditor with Editor.from_token(baseurl=kwargs['sessionUrl'], token=kwargs['sessionToken']) as tiseditor: # Getting the descriptor ID of the treenode using the path get_resolve_response = tiseditor.api.get_resolve("%2FOwnerUserName%2FFolderName%2FPageName") descriptor_id = get_resolve_response[1]["Id"] # Creating permission for the treenode response_set_permissions=tiseditor.api.set_permissions(user_id="UserName", permission_type="Read,Write", grant_type="Allow/Deny", inheritance=True, descriptor_id=descriptor_id) # Getting the permission of an user regarding a treenode permission=tiseditor.api.get_permissions(user_guid="UserName", descriptor_id=descriptor_id)TIS-Editor: calculate differences between data-tables (even with different columns):
Compare two data-nodes (even if they have different columns):
- identify records to compare with key-columns
- select a set of columns and get a nice report on differences
- One can define several such sets
"""Suche Unterschiede im Journal des AZ-Rechners."""# # Das Original liegt im GIT auf:## UnterschiedeSuchenInJournal.py# C:\_calcuLex\calcuLex\AZR_200901 <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<## inkl. Tests ...## ERGEBNIS: im AUFBAU NEUe Liste wird mit alter Liste verglichen# # WICHTIG: Spalten zum Vergleich auf gleich ungleichKEYS_COLUMNS = ['Von', 'Bis', 'Typ']###import datetimeimport copyimport difflibimport pprintdef addcolumn(name, type, types, columns): """Ergänzt Spaltendefinition.""" if name not in columns: columns.update({name:len(columns)}) types.update({len(types):type}) return columns[name]def compare_keys(v_a,v_n, columns, columns_n): """Vergleicht Keyspalten und gibt das zurück was vorher dran ist, oder ident.""" if v_a == [] and v_n == []: return 'Error - beides leer' elif v_a == []: return 'neu' elif v_n == []: return 'alt' for x in KEYS_COLUMNS: if v_a[columns[xTIS 6.6 samples
Get all files and tables using pytisapi
## run routine (allows accessing data synchronously and asynchronously)#async def run(params, intables, outtables, infiles, outfiles, misc): # pytisapi import pytisapi from pytisapi.editormapper.editor import Editor from pytisapi.editormapper.tabletreenode import TableTreeNode result = [] try: with Editor.from_token(baseurl=misc.session_url, token=misc.session_token) as editor: # get all projects projects = editor.get_projects() for project in projects: result.append(['Project', str(project)]) # get all files files = get_files([], "", editor.get_fileroot()) for file in files: result.append(['File', file]) # get all tables tables = get_tables([], "", TableTreeNode(-1, None, editor.api)) for table in tables: result.append(['Table', table]) except pytisapi.TISApiException as e: print("failed with %r" % (e)) return ### read/write parameters #param1 = params['param1'] #params['param1'] = 'new param value' ### read input table 0 synchronously #cols = intables[0].columns #types = intables[0].types #rows = await intables[0].rows() ### read input table 1 asynchronously #cols = intables[1].columns #types = intables[1].types #async for row in intables[1].rows_async(): # pass ### write output table 0 (operator result table) synchronously outtables[0].columns = { 'ObjectType': 0, 'Name': 1 } outtables[0].types = { 0: str , 1: str} outtables[0].rows = result ### write output table 1 synchronously #outtables[1].columns = { 'Col 1': 0, 'Col 2': 1 } #outtables[1].types = { 0: str, 1: int } #rows = [ [ 'asdf', 3 ], [ 'opqw' , -1 ] ] #for row in rows: # await outtables[1].send_row(row) ### read input file 0 synchronously #textreader = await infiles[0].textreader() #args: encoding='UTF-8', errors='strict', newline='\r\n' #for line in textreader: # line.strip('\r\n') # read input file 1 asynchronously #textreader = infiles[1].textreader_async() #args: encoding='UTF-8', errors='strict', newline='\r\n' #async for line in textreader: # line.strip('\r\n') ### write output file 0 synchronously #textwriter = outfiles[0].textwriter() #args: encoding='UTF-8', errors='strict' #lines = [ 'test output 0 line 1\n', 'test output 0 line 2\n' ] #textwriter.writelines(lines) ### write output file 1 asynchronously #textwriter = outfiles[1].textwriter_async() #args: encoding='UTF-8', errors='strict' #for line in lines: # await textwriter.writelines_async(line) ### access miscellaneous info (timeout, version, session_url, session_token) #print('Session URL: %s' % misc.session_url) #print('Session token: %s' % misc.session_token)# recursive function to get all files in specified treenodedef get_files(files, path, filetreenode): children = filetreenode.get_children_list() attrs = filetreenode.get_attrs() current_path = path + "\\" + attrs['Caption'] if children: for child in children: child_attrs = child.get_attrs() if child_attrs['Type'] == 'Folder': get_files(files, current_path, child) else: files.append(current_path + "\\" + child_attrs['Caption']) return files # recursive function to get all tables in specified treenodedef get_tables(tables, path, tabletreenode): children = tabletreenode.get_children_list() attrs = tabletreenode.get_attrs() current_path = path + "\\" + attrs['Caption'] if children: for child in children: child_attrs = child.get_attrs() if child_attrs['Type'] == 'Folder': get_tables(tables, current_path, child) else: tables.append(current_path + "\\" + child_attrs['Caption']) return tables TIS 6.7 samples
Upload a file via pytisapi
Upload a file
def create_table(params, types, columns, files):types[0] = strcolumns['Result'] = 0inreader = files.i[0].bytereader()contents = inreader.read()for ofile in files.o:bytewriter = ofile.bytewriter()bytewriter.write(contents)return [ ["Synchronized %d files" % len(files.o)]] Download a file via pytisapi
Download a file
prj.open() filepathdto={ "clientId": "01", "fullFilePath":"FLEX-7771\\flex_7325.csv" } file_id=prj.api.get_fileid_from_filepath(filepathdto) token = prj.api.download_file_token(file_id) resp=prj.api.download_file(token) with open("C:/Install/download.csv", 'wb') as f: for chunk in resp.iter_content(chunk_size=1024): if chunk: f.write(chunk) f.flush() Access profiler information via pytisapi
Access profiler information
import pytisapifrom pytisapi.editormapper.editor import Editorresult_columns = ["Type", "TimeStamp", "Description", "ClientId", "UserId", "ProjectId", "ProjectName", "GrossCalcDuration", "NetCalcDuration", "RecalcDepth", "DataNodeId", "DataNodeCaption", "OpId", "OpCaption", "StartTableColCount", "StartTableRowCount", "CurrentMemoryConsumption", "CustomData", "RecalcNecessary", "IsLastRunByUser"]def convert_entry(l): return [l[o] for o in result_columns] async def create_table(params, types, columns, files): with Editor.from_token(baseurl=kwargs['sessionUrl'], token=kwargs['sessionToken'], verify=False) as editor: status, activitylogs = editor.api.get_activity_log() for i, colname in enumerate(result_columns): columns[colname] = i for el in activitylogs["Items"]: yield convert_entry(el) Generate test data from data node
Generate testdata for python tests and debugging based on existing TIS nodes (code and example result)
"""Einfache Erzeugung von Testdaten für python-Entwicklung von simple-mains o.ä. aus TIS heraus. Default alle columns aber einschränkbar."""# C:\_calcuLex\calcuLex\simple_main_collection\simple_testdata_Generierung.py# CHANGE LOG# 2023 10 24 Null Objekte werden in None übersetzt# **** HAUPTERGEBNIS: TESTDATEN in python mylist geschrieben, mit den gewählten Spalten (siehe Einstellungen).# **** ZUSATZERGEBNISSE: Entsprechende columns, types dictionaries und eine python Klasse, die den Zugriff auf Spalten erleichtert, einige Infos.# **** NUTZUNG: python Operator anlegen, dieses Skript hinein, Einstellungen anpassen, Export in EXCEL# **** Empfehlenswert: FormelOP (ohne Ergebnisspalte!!!) vor Python und Parameter: # XIH.SetParam("Info aufrufender Knoten etc", "Datenherkunft SERVER:" + XIH.ServerName() + " PROJEKT: " + XIH.ProjectName() + " KNOTEN: " + XIH.NodeName() + " USER: " + XIH.UserName() )# FALLWEISE: müssen Texte mit Seitenumbrüchen manuell entfernt werden.# **** EINSTELLUNGEN:# SELECT_ALL_COLUMNS = True# Alternativ: Spaltennamen jener Spalten in Select_Columns, die in TIS Daten vorhanden sind und übernommen werden sollen. Reihenfolge egal, nur Name wichtig.# Die Spaltennamen werden auch in Output gelistet, sodass sie bei Auswahl kopiert werden können. SELECT_ALL_COLUMNS = True # führt dazu, dass egal was in coluns steht, alle genommen werden sonst nur definierte Liste# Select_Columns = ['Von', 'Bis', 'ID_Abwesenheitsgrund', 'Länge Ruhezeit vorher wenn Ruhezeit endet', 'Beginn AZ Tag', 'NAZ Std KalTag', 'Infos zum Zeitausgleich', 'Typ'] ZEILE_VON = 0 # optionalZEILE_BIS = 9999 # OptionalPARAMETER_MIT_PFADEN_NICHT_EXPORTIEREN = True # Reduziert Formatfehler EXCLUDE_PARAMETERS = ['TabellePfadUsermanagement', 'ReplaceCharacters', 'PFAD_Eingaben', 'TabellePfad', 'TabellePfadGlobal', 'PDF_Path' ]EINRÜCKEN_DATEN_KOLLABIERBAR = True # Optional: True führt zu Bereich, der eingeklappt werden kann.# AB HIER KEINE ÄNDERUNGEN ERFORDERLICHimport copyimport datetimedef addcolumn(name, type, columns, types): """Spalte dazu.""" index = len(columns) columns.update({name:len(columns)}) types.update({len(types):type}) return indexdef prettyString(txt): """Entfernt Sonderzeichen.""" res = 'c_' for c in txt: res += c if str.isalnum(c) else '_' return resdef prefix(): """Generiert Prefix.""" if EINRÜCKEN_DATEN_KOLLABIERBAR: return ' ' else: return ''def print_header(mylist, colu_in, params): """Allgemeine Tesdatengenerierungsinfo.""" # # allgemeine Infos mylist.append('#') mylist.append('# Testdatengenerierung ausgewählter Spalten und Klasse, die den Zugriff auf Spalten vereinfacht.') mylist.append('# C:\_calcuLex\calcuLex\simple_main_collection\simple_testdata_Generierung.py') mylist.append('#') mylist.append('# Daten erzeugt am: ' + str(datetime.datetime.now())) if 'Info aufrufender Knoten etc' in params: mylist.append('# ' + params['Info aufrufender Knoten etc'] ) mylist.append('#') # ausgewählte Spalten drucken - Info zu Einstellungen txt = " '" + Select_Columns[0] + "'" for i in range(1, len(Select_Columns)): txt += ", '" + Select_Columns[i] + "'" mylist.append('# Für Select_Columns = [' + txt + ']') mylist.append('#') # vorhandene Spalten drucken - erleichtert es, später Spalten zu ergänzen txt = "" for i,c in enumerate(colu_in): txt += '' if i== 0 else ', ' txt += "'" + c + "'" mylist.append('# Aus vorh. Spaltennamen = [' + txt + ']') mylist.append('#') mylist.append('# Standardimports') mylist.append('import datetime') mylist.append('import copy')def print_colClass (mylist, colu_in): """Generiert Klasse, die Spaltenzugriff erleichtert.""" mylist.append('') mylist.append('class class_colNrs:') mylist.append(' """Zuweisung Spaltennummer für Originaldaten in TIS. Aufruf mit colNrs = class_colNrs(columns)."""') mylist.append('') mylist.append(' def __init__(self, columns):') mylist.append(' """Init der Klasse mit Zuordnung der Nummern."""') for c in Select_Columns: mylist.append(' self.' + prettyString(c) + " = columns['" + c + "']") mylist.append('') mylist.append('# dieses Objekt kennt dann die Testdatenspalten, praktisch bei Programmierung') mylist.append('colNrs = class_colNrs(columns)') mylist.append('') def print_columns (mylist, colu_in): """Weist ausgewählte Spalten in erzeugten Testdaten zu.""" mylist.append('') mylist.append('columns={}') mylist.append('' if not EINRÜCKEN_DATEN_KOLLABIERBAR else 'if True:') for i, c in enumerate(Select_Columns): mylist.append(prefix() + 'columns["' + str(c) + '"] = ' + str(i)) i += 1 mylist.append('') def print_params (mylist, params): """Bereitet leere Liste für Parameter vor.""" mylist.append('') mylist.append('params = {}') mylist.append('') for k in sorted(list(params.keys()), key = str.lower): if not PARAMETER_MIT_PFADEN_NICHT_EXPORTIEREN or type(params[k]) != str or '\\' not in params[k]: if k not in EXCLUDE_PARAMETERS: mylist.append("params['" + k + "'] = " + __Print_value(params[k])) def print_types (mylist, colu_in, type_in): """Weist ausgewählte Typen in erzeugten Testdaten zu.""" mylist.append('') mylist.append('types ={}') mylist.append('' if not EINRÜCKEN_DATEN_KOLLABIERBAR else 'if True:') for i, c in enumerate(Select_Columns): if c in colu_in: mylist.append(prefix() + 'types [' + str(i) + '] = ' + str(type_in[colu_in[c]]).replace("<class '","").replace("'>","")) else: mylist.append(prefix() + 'types [' + str(i) + '] = Column not found: ' + c) mylist.append('') def __Print_value(val) -> str: """Druck als python.""" res = '' if type(val) == datetime.datetime: res = 'datetime.datetime(' + str(val.year) + ', ' + str(val.month) + ', ' + str(val.day)+ ', ' + str(val.hour) + ', ' + str(val.minute) + ', ' + str(val.second) + ')' elif type(val) == datetime.date: res = 'datetime.date(' + str(val.year) + ', ' + str(val.month) + ', ' + str(val.day) + ')' elif type(val) == datetime.time: res = 'datetime.time(' + str(val.hour) + ', ' + str(val.minute) + ', ' + str(val.second) + ')' elif type(val) == str: res = "'" + val + "'" else: res = str(val) return resdef print_data(mylist, myli_in, colu_in): """Tesdaten drucken.""" mylist.append('') mylist.append('mylist = []') mylist.append('' if not EINRÜCKEN_DATEN_KOLLABIERBAR else 'if True:') mylist.append('' if not EINRÜCKEN_DATEN_KOLLABIERBAR else ' pass') # Sicherheit falls Liste leer for i, v in enumerate(myli_in): if i >= ZEILE_VON and i <= ZEILE_BIS: txt = prefix() + 'mylist.append([' for c in Select_Columns: if c != Select_Columns[0]: txt += ', ' if c in colu_in: neu = __Print_value(v[colu_in[c]]) if "<XIMES." in neu and "NullType object at 0x" in neu: neu = "None" txt += neu else: txt += 'Column not found: ' + c mylist.append(txt + '])')def simple_main(params, mylist, types, columns): """Generierung phython Zeilen.""" # columns, types, mylist erhalten und anders befüllen für Rückgabe in TIS colu_in = copy.deepcopy(columns) type_in = copy.deepcopy(types) myli_in = copy.deepcopy(mylist) mylist.clear() columns.clear() types.clear() global Select_Columns # Generierung SELECT COLUMNS if SELECT_ALL_COLUMNS: Select_Columns = [*colu_in] #generiert Liste aller keys print (Select_Columns) print (type_in) # Neuer Inhalt in TIS addcolumn('Testdaten', str, columns, types) # Erzeugung print_header (mylist, colu_in, params) print_columns (mylist, colu_in) print_types (mylist, colu_in, type_in) print_params (mylist, params) print_data (mylist, myli_in, colu_in) print_colClass(mylist, colu_in) return mylist# ********************************* EXAMPLE RESULT ***********************************# ## # Testdatengenerierung ausgewählter Spalten und Klasse die den Zugriff auf splatn verenfacht# # C:\_calcuLex\calcuLex\simple_main_collection\simple_testdata_Generierung.py# ## # Daten erzeugt am: 2022-01-28 13:51:52.829162# # Für SELECT_COLUMNS = [ 'Von', 'Bis', 'ID_Abwesenheitsgrund', 'Länge Ruhezeit vorher wenn Ruhezeit endet', 'Beginn AZ Tag', 'NAZ Std KalTag', 'Infos zum Zeitausgleich', 'Typ']# ## # Aus vorh. Spaltennamen = ['Woche', 'Zeitart', 'Von', 'Bis', 'ZNr AZ roh', 'ZNr Intervall', 'ZNr Intervall2', '01 Arbeit in vereinbarter Lage NormalAZ', '023 Angeordnete Überstunden', '02 Arbeit ....... 'Überstunden Art', 'Wochentag_1', 'Wochentag_2', 'Kalendertag']# ## columns={}# columns['Von'] = 0# columns['Bis'] = 1# columns['ID_Abwesenheitsgrund'] = 2# columns['Länge Ruhezeit vorher wenn Ruhezeit endet'] = 3# columns['Beginn AZ Tag'] = 4# columns['NAZ Std KalTag'] = 5# columns['Infos zum Zeitausgleich'] = 6# columns['Typ'] = 7# types ={}# types [0] = datetime.datetime# types [1] = datetime.datetime# types [2] = str# types [3] = float# types [4] = datetime.datetime# types [5] = float# types [6] = str# types [7] = str# params = []# mylist = []# mylist.append([datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 1, 9, 0, 0), datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 1, 12, 30, 0), 'keinEintrag', 105.0, datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 1, 9, 0, 0), 8.0, 'xx', 'Typ_AZexklÜStd'])# mylist.append([datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 1, 13, 0, 0), datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 1, 16, 30, 0), 'keinEintrag', 0.5, datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 1, 9, 0, 0), 8.0, 'xx', 'Typ_AZexklÜStd'])# mylist.append([datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 2, 9, 0, 0), datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 2, 12, 30, 0), 'keinEintrag', 16.5, datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 2, 9, 0, 0), 8.0, 'xx', 'Typ_AZexklÜStd'])# mylist.append([datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 2, 13, 0, 0), datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 2, 16, 30, 0), 'keinEintrag', 0.5, datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 2, 9, 0, 0), 8.0, 'yy', 'Typ_AZexklÜStd'])# mylist.append([datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 4, 9, 0, 0), datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 4, 12, 30, 0), 'keinEintrag', 40.5, datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 4, 9, 0, 0), 8.0, '-', 'Typ_AZexklÜStd'])# mylist.append([datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 4, 13, 0, 0), datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 4, 16, 30, 0), 'keinEintrag', 0.5, datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 4, 9, 0, 0), 8.0, '-', 'Typ_AZexklÜStd'])# mylist.append([datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 5, 9, 0, 0), datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 5, 12, 30, 0), 'keinEintrag', 16.5, datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 5, 9, 0, 0), 8.0, '-', 'Typ_AZexklÜStd'])# mylist.append([datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 5, 13, 0, 0), datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 5, 16, 30, 0), 'keinEintrag', 0.5, datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 5, 9, 0, 0), 8.0, '-', 'Typ_AZexklÜStd'])# mylist.append([datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 7, 9, 0, 0), datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 7, 12, 30, 0), 'keinEintrag', 40.5, datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 7, 9, 0, 0), 8.0, '-', 'Typ_AZexklÜStd'])# mylist.append([datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 7, 13, 0, 0), datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 7, 16, 30, 0), 'keinEintrag', 0.5, datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 7, 9, 0, 0), 8.0, '-', 'Typ_AZexklÜStd'])# mylist.append([datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 8, 9, 0, 0), datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 8, 12, 30, 0), 'keinEintrag', 16.5, datetime.datetime(2021, 10, 8, 9, 0, 0), 8.0, '-', 'Typ_AZexklÜStd'])# class class_colNrs:# """Zuweisung Spaltennummer für Originaldaten in TIS. Aufruf mit colNrs = class_colNrs(columns)."""# def __init__(self, columns):# """Init der Klasse mit uordnung der Nummern."""# self.c_Von = columns['Von']# self.c_Bis = columns['Bis']# self.c_ID_Abwesenheitsgrund = columns['ID_Abwesenheitsgrund']# self.c_Länge_Ruhezeit_vorher_wenn_Ruhezeit_endet = columns['Länge Ruhezeit vorher wenn Ruhezeit endet']# self.c_Beginn_AZ_Tag = columns['Beginn AZ Tag']# self.c_NAZ_Std_KalTag = columns['NAZ Std KalTag']# self.c_Infos_zum_Zeitausgleich = columns['Infos zum Zeitausgleich']# self.c_Typ = columns['Typ']# # dieses Objekt kennt dann die Testdatenspalten, praktisch bei Programmierung# colNrs = class_colNrs(columns)Generate an SQL SELECT Statement using the columns-definitions of a data-node (e.g. for complex queries using SQL)
Generate an SQL SELECT Statement using the columns-definitions of a data-node (e.g. for complex queries using SQL)
"""Einfache Erzeugung von SQL-Queries aus TIS heraus um Spalten von TIS nicht abtippen zu müssen."""# C:\_calcuLex\calcuLex\simple_main_collection\simple_SQL_Import_Generierung.py# **** HAUPTERGEBNIS: SQL Statement, dass bestehender Knotenstruktur entspricht - zB wenn TIS-Import durch SQL Import ersetzt werden soll (z.B. aus anderem Tablespae, mit merge ...)# **** NUTZUNG: python Operator anlegen, dieses Skript hinein, Einstellungen anpassen, Export in EXCEL# ACHTUNG: Erfordert für BenutzerIn die BERECHTIGUNG SQLImportDAL, um dann das SQL Script einzuspielen (eventuell Ab & wieder Anmelden erforderlich)# **** EINSTELLUNGEN:SHORT_NAME_TABLE = 'T' # Wenn statt Tabellen_iD == 'T ein Leerstring verwendt wird, dann wird 'T.C0 ... zu C0ALLE_C_DEFINITIONEN_IN_EINE_ZEILE = False # Wenn True dann einfacher in eine Zelle zu kopieren. Standardfall = False# AB HIER KEINE ÄNDERUNGEN ERFORDERLICHimport copyimport datetimedef addcolumn(name, type, columns, types): """Spalte dazu.""" index = len(columns) columns.update({name:len(columns)}) types.update({len(types):type}) return indexdef prettyString(txt): """Entfernt Sonderzeichen.""" res = 'c_' for c in txt: res += c if str.isalnum(c) else '_' return resdef print_header(mylist, colu_in): """Allgemeine Tesdatengenerierungsinfo.""" # # allgemeine Infos mylist.append('') mylist.append('/* SQL-Generierung ausgewählter Spalten zB bei Ersatz TIS-Read durch SQL. */') mylist.append('/* C:\_calcuLex\calcuLex\simple_main_collection\simple_SQL_Import_Generierung.py */') mylist.append('') mylist.append('/* Daten erzeugt am: ' + str(datetime.datetime.now()) + '*/') mylist.append('') def simple_main(params, mylist, types, columns): """Generierung phython Zeilen.""" # columns, types, mylist erhalten und anders befüllen für Rückgabe in TIS colu_in = copy.deepcopy(columns) mylist.clear() columns.clear() types.clear() # Neuer Inhalt in TIS addcolumn('Testdaten', str, columns, types) # Erzeugung print_header (mylist, colu_in) mylist.append('SELECT') i = 0 cx_txt = '' for c in colu_in.keys(): new_txt = ' ' + (SHORT_NAME_TABLE + '.' if SHORT_NAME_TABLE != '' else '') + 'C' + str(i) + ' "' + c + '"' + (',' if i < len(colu_in)-1 else ' ') if ALLE_C_DEFINITIONEN_IN_EINE_ZEILE: cx_txt += new_txt else: mylist.append(new_txt) i +=1 mylist.append(cx_txt) # Sonst Leerzeile mylist.append(" FROM #XI.TISTable(#XI.TISPar('MAIN\FOLDER1')#, #XI.TISPar('TAB1')#)# " + SHORT_NAME_TABLE) return mylist# EXAMPLE RESULT (with adapated path & table) with SHORT_NAME_TABLE = 'T' and ALLE_C_DEFINITIONEN_IN_EINE_ZEILE = False # SELECT# T.C0 "Zuschlag Art",# T.C1 "Von",# T.C2 "Bis",# T.C3 "Mo",# T.C4 "Di",# T.C5 "Mi",# T.C6 "Do",# T.C7 "Fr",# T.C8 "Sa",# T.C9 "So",# T.C10 "Feiertag",# T.C11 "Bezeichnung falls Zusatzbedingung",# T.C12 "Betrag",# T.C13 "Prozent",# T.C14 "Anmerkung",# T.C15 "Quelle (zB KV, Jahr, Version)",# T.C16 "Gültig ab 0 Uhr des Datums",# T.C17 "Gültig bis 24 Uhr des Datums" # FROM #XI.TISTable('AZ Erfassung\AZV03\Data', 'AZ_Fertig_03')# T# EXAMPLE RESULT (with adapated path & table) with SHORT_NAME_TABLE = '' and ALLE_C_DEFINITIONEN_IN_EINE_ZEILE = True # SELECT# C0 "Faktor", C1 "FILIALE", C2 "Von", C3 "Bis", C4 "Wert", C5 "DO NOT USE TAG", C6 "Anzahl Tage mit Werten", C7 "Woche", C8 "Use | Tage mit Werten", C9 "DO NOT USE WOCHE", C10 "PB", C11 "Woche im Monat", C12 "Berechnungsdatum", C13 "Monat", C14 "Quelle"# FROM #XI.TISTable(#XI.TISPar('MAIN\FOLDER1')#, #XI.TISPar('TAB1')#)#TIS 6.9 samples
Using pytisapi to get TIS Table
This sample shows how to use pytisapi to get all the data and properties from a TIS Results-Table
# pytisapiimport pytisapifrom pytisapi.editormapper.editor import Editortry: with Editor.from_token(baseurl=kwargs['sessionUrl'], token=kwargs['sessionToken']) as editor: projects = editor.get_projects() project_name ='Project A' dn_name = 'A00 Data node' project = projects[project_name] dns = project.get_datanodes() dn = dns[dn_name] full_table = dn.get_full_table() for key in dn._fulltable.keys(): print(full_table[key])Using pytisapi for recalculating data nodes asynchronously
This sample shows how to use pytisapi to start a data node calculation in a subsession asynchronously
def create_table(params, types, columns, files): # pytisapi import pytisapi from pytisapi.editormapper.editor import Editor result = [] try: # use of 'asyncSession=True' argument in 'from_token' method with Editor.from_token(baseurl=kwargs['sessionUrl'], token=kwargs['sessionToken'], asyncSession=True) as editor: projects = editor.get_projects() # --- iteration 1 project_name ='Project A' dn_name = 'A00 Data node' project = projects[project_name] dns = project.get_datanodes() dn = dns[dn_name] task_id = dn.recalculate(wait=False) # <- wait=False, so this method returns immediately print(task_id) _, resp = editor.api.get_task(task_id) print(resp) result.append([project_name, dn_name, resp['StartTime'], resp['EndTime'], resp['Status']]) # --- except pytisapi.TISApiException as e: print("failed with %r" % (e)) return return resultMerge python files into one to reduce upload and maintenance work
Allows to merge python files into one to reduce upload and maintenance work
from argparse import ArgumentParserfrom pathlib import Pathfrom datetime import datetimerelpath = Path(__file__).parentSHELL_MODE = FalseFILEPATHS = [ # relpath is the directory that this file is in. # add files like this relpath/"file.py" # order the files are generated is the same as they appear in this list! relpath/'..'/"cx.py", relpath/'..'/"helper_Zeiten_allg.py",]SUFFIX = datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M")FILENAME = "_merged_"PREFIX = "AZR220828"def build_file(pre, suffix: str, files): print(f"{pre}-{suffix}::{files}") filename = relpath/f"{pre}{FILENAME}{suffix}.py" sfilename = str(filename) with open(sfilename, "w+") as outfile: outfile.write(f"# generated on {datetime.now().isoformat()} \n") outfile.write(f"# filenames are relative to: {relpath}\n" ) outfile.write(f"# see ticket AZR-483 for documentation\n") for file in files: outfile.write(f"# included file: {str(file)}\n") for file in files: outfile.write("#" + ("=" * 40) + "\n") outfile.write("#" + f"merging file: {str(file)}".center(40) + "\n") outfile.write("#" + ("=" * 40) + "\n") with open(str(file), "r") as input_file: outfile.write(input_file.read())if SHELL_MODE: parser = ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument("-s", "--suffix", help="suffix to use for the generated file.") parser.add_argument("-o", "--outdir", help="Directory to store the resulting file.") parser.add_argument("-p", "--prefix", help="prefix for the fiile to use") parser.add_argument("files", nargs="+") args = parser.parse_args() build_file(args.prefix or "", args.suffix or "", args.files)else: build_file(PREFIX, SUFFIX, FILEPATHS)Validate fields of a TIS Board form
Validate fields of a TIS Board form
"""Validate fields of a TIS Board form.Each row represents one field.Field is identified by string contained in column 'ID'.ID_ERRFUNC attaches a validation function to each ID.Validation functions return a tuple with an error text and an error code. """import jsonFORM_INPUT_FIELD_MAPPINGS = { "String": "Value String", "DayOfWeek": "Value String", "TimestampConstraint": "Value String", "DurationConstraint": "Value String", "SingleDuration": "Value String", "HalfDurationConstraint": "Value String", "Selection": "Value String", "Selection2": "Value String", "HalfDurationConstraint": "Value String", "FloatConstraint": "Value String", "IntConstraint": "Value String", "HalfFloatConstraint": "Value String", "Zahl": "Value Float", "Double": "Value Float", "Bool": "Value Bool", } def validation_name(name: str): if not name: return (f'Name cannot be empty.', 2) return ('',0)def validation_compulsory_selection(input: str): error_msg = f"No value selected." selected = None for item in json.loads(input): if item["Selected"]: selected = item["Name"] if not selected: return (error_msg, 2) return ('',0) ID_ERRFUNC = { "Name": validation_name, "Select me": validation_compulsory_selection, }async def run(params, in_tables, out_tables, in_files, out_files, misc): i0_table_form = in_tables[0] o0_table_form_validated = out_tables[0] columns = i0_table_form.columns o0_table_form_validated.columns = columns o0_table_form_validated.types = i0_table_form.types in_table = list(await i0_table_form.rows()) for row in in_table: out_row = list(row) data_type = row[columns["Data type"]] data = row[columns[FORM_INPUT_FIELD_MAPPINGS[data_type]]] error_msg, error_code = ID_ERRFUNC.get(row[columns["ID"]], lambda x: ("", 0))(data) out_row[columns["Error text"]]= error_msg out_row[columns["Error code"]]= error_code await o0_table_form_validated.send_row(out_row) Start subprocesses, e.g. to Copy tables between databases from python
Start subprocesses, e.g. to Copy tables between databases from python
import osimport subprocesssqlplus_script_DROP = """connect .... user... drop synonym xx_table;exit"""KOPIEREN_STATT_DROPPEN = Truesqlplus_script_COPY = """COPY FROM .... user... TO .... user2... REPLACE xx_table USING SELECT * from xx_table;COMMIT;exit"""TABLES = [ 'yyyy', 'zzz' ]def simple_main(params, mylist, types, columns): for t in TABLES: if KOPIEREN_STATT_DROPPEN: sc = sqlplus_script_COPY.replace('xx_table', t) else: sc = sqlplus_script_DROP.replace('xx_table', t) print ('t', t) print ('SC', sc) # C:\client\product\19.0.0\client_1\bin\ p = subprocess.Popen (['sqlplus.exe', '/nolog'] \ , stdin = subprocess.PIPE \ , stdout = subprocess.PIPE \ , stderr = subprocess.PIPE) (stdout,stderr) = p.communicate(sc.encode('utf-8')) stdout_lines = stdout.decode('utf-8').split("\n") print ('KOPIERT: ' + t) return mylist TIS 7.0 Examples
Return numpy values from a Python operator (note: numpy has to be added using additional packages during deployment)
Return numpy values from a Python operator (note: numpy has to be added using additional packages during deployment)
import numpy as npdef create_table(params, types, columns, files): types[0] = str types[1] = float columns['Operation'] = 0 columns['Mean'] = 1 a = np.array([1e8]*1000) return [ # this will fail: # ["Sum", np.sum(a, dtype=np.int64)], # Getting native type with .item() works ["Sum", np.sum(a, dtype=np.int64).item()] ] Using pytisapi, set all datanodes in a project to "Fixed"
Using pytisapi, set all datanodes in a project to "Fixed".
import pytisapifrom pytisapi.editormapper.datanode import Datanodedef freeze_data_nodes(project_datanodes: dict[str, Datanode], folder_node): """Traverses the folder hierarchy given by 'folder_node' recursively. All data nodes found are set to fixed.""" for child in folder_node.get_children_list(): if child.is_datanode(): node_name = child.attrs['Caption'] datanode = project_datanodes[node_name] if datanode.attrs['Fixed']: print("Already fixed: " + node_name) else: datanode.set_fixed(True) # Freeze the node else: freeze_data_nodes(project_datanodes, child)pname = "Project A"with pytisapi.editormapper.editor.Editor.from_credentials("<url>", "<user>", "<password>", "01") as tiseditor: projects = tiseditor.get_projects() project = projects[pname] freeze_data_nodes(project.get_datanodes(), project.get_projecttree())