Sum and count
Summary
Time intervals are assigned to calendar periods (e.g. per month, per quartile) and the following analyses are supported:
- Summation of durations (if necessary weighted by value)- “e.g. 3 persons present for 4 hrs on day X: equals 12 hrs on day X
- Summation of values – ‘’e.g. 30 € + 20 € turnover on day X: equals 50 € on day X
- Counting – ‘’e.g. 30€ + 20€ sales volume on day X: equals 2 sales on day X
Configuration
Input settings of existing table
Name | Value | Opt. | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Identifier | System.Object | opt. | Which columns should be evaluated for the identifier? | - |
Date + time (from) | System.DateTime | - | Column containing the start (date+time) of the time interval. | - |
Date + Time (to) | System.DateTime | - | Column containing the end (date+time) of the time interval. | - |
Calculate totals field | System.Object | opt. | Columns whose values are used for the 'summarized by' calculation. | - |
Settings
Name | Value | Opt. | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Scaling | System.String
| - | Scaling specification, e.g. Weeks, months... | - |
Calculation method | System.String
| - | Selection of how the time interval is allocated. | - |
Totals field | System.String
| - | Which function should be applied to the data? (add up hours or events) | - |
Time Unit | System.String
| - | Select the time unit in which the time span of the data are to be calculated (hours, days...) | - |
Remarks
- This operation requires the data to be converted to a standardised time format: Please refer to Convert "From-Date/From-Time/To-Time"
- Please also refer to Operation Scaling, which allows similar calculations for shorter time intervals (e.g. employees present from 2 pm to 2,30 pm on day X).
- Several columns with numbers can be summarized at the same time (e.g. when several number columns are summarized).
Want to learn more?
Time periods are set in a specific scale (e.g. Per month, per quarter).
Screenshot
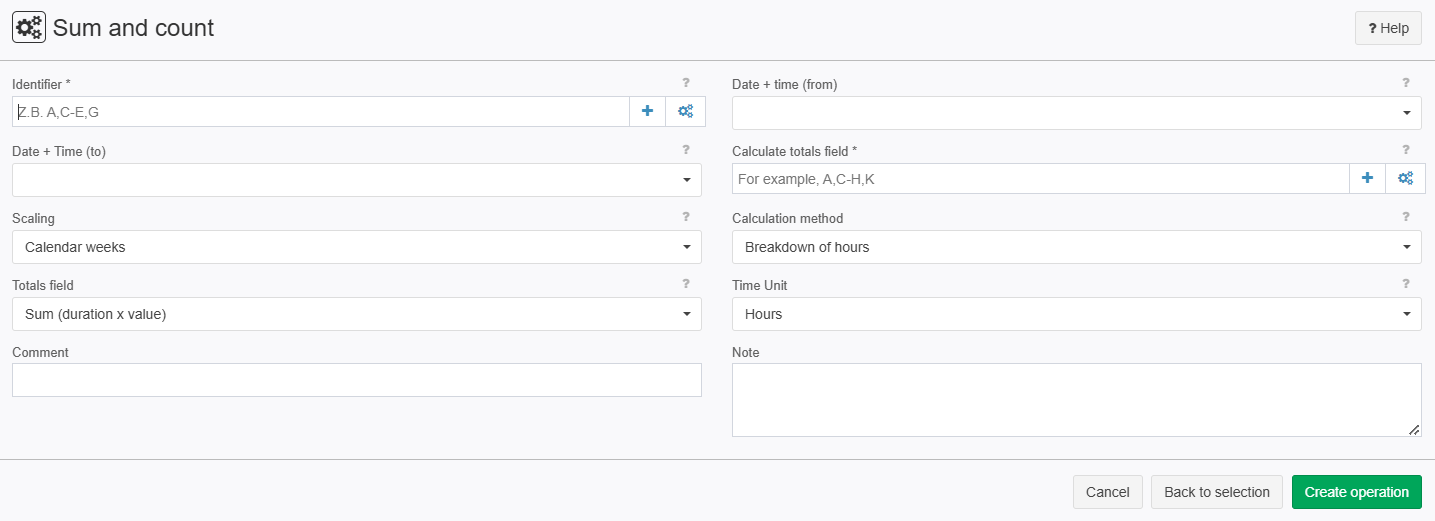
Examples
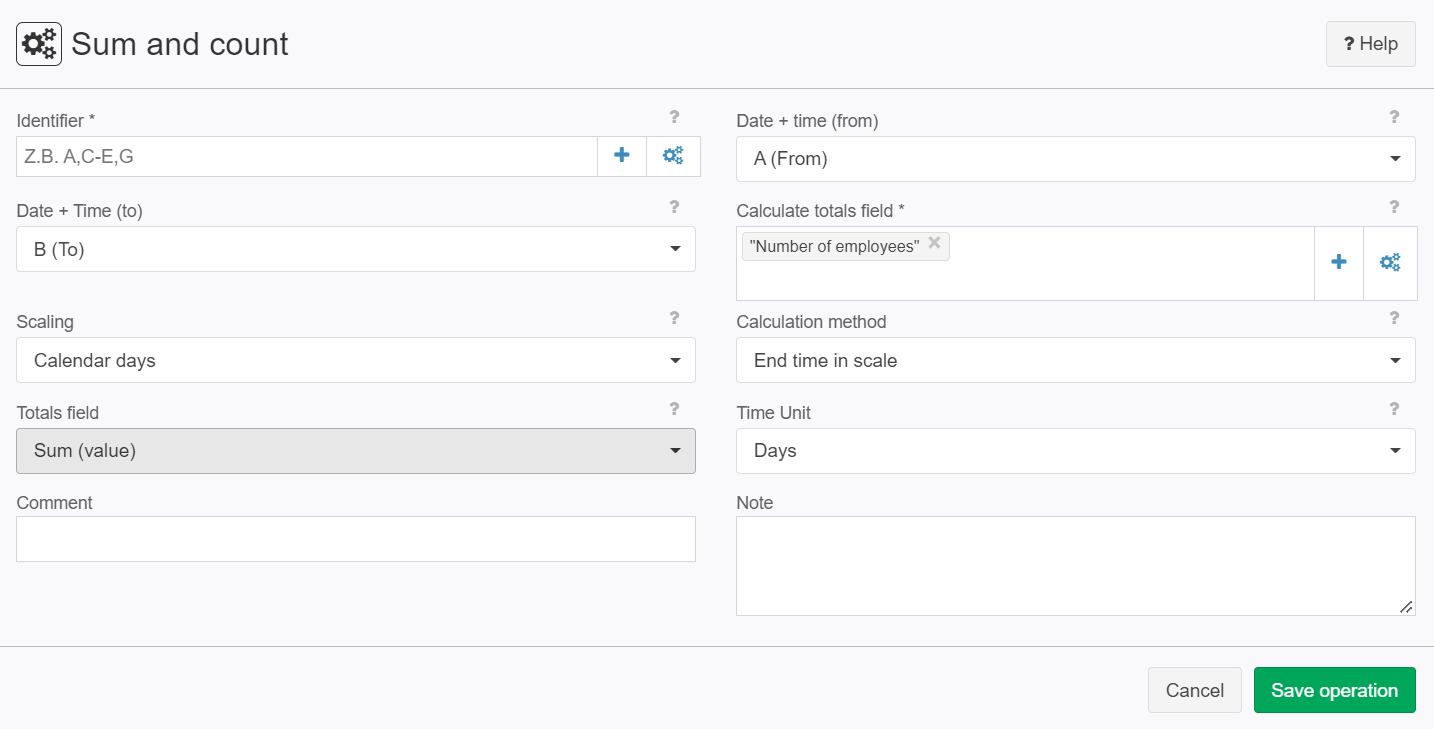
Example: Sum (value)
Situation | The following input record shall be analysed for summation (value):
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Settings |
| ||||||||||||
Result |
| ||||||||||||
Project File | - |
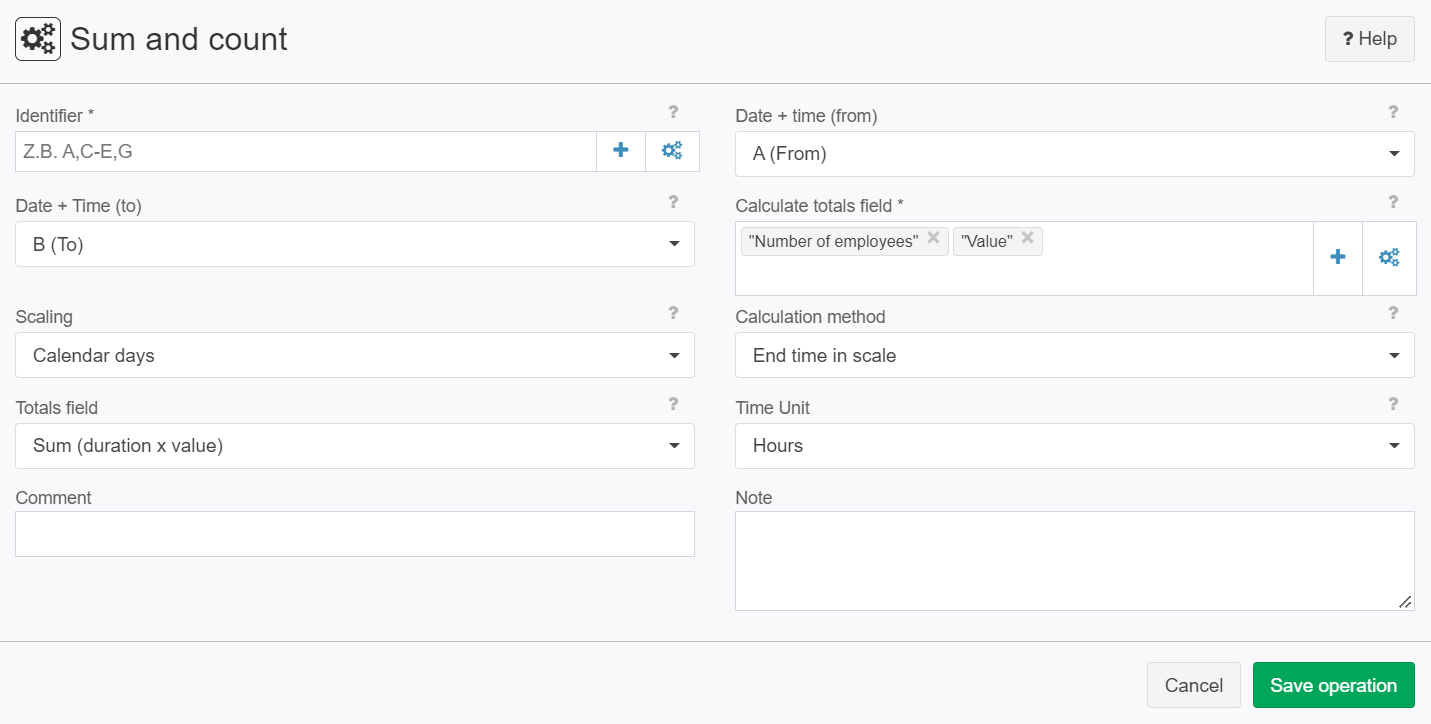
Example: Sum (Time period x value)
Situation | The following input record shall be analysed for summation (time period x value):
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Settings |
| |||||||||||||||
Result |
| |||||||||||||||
Project File | - |
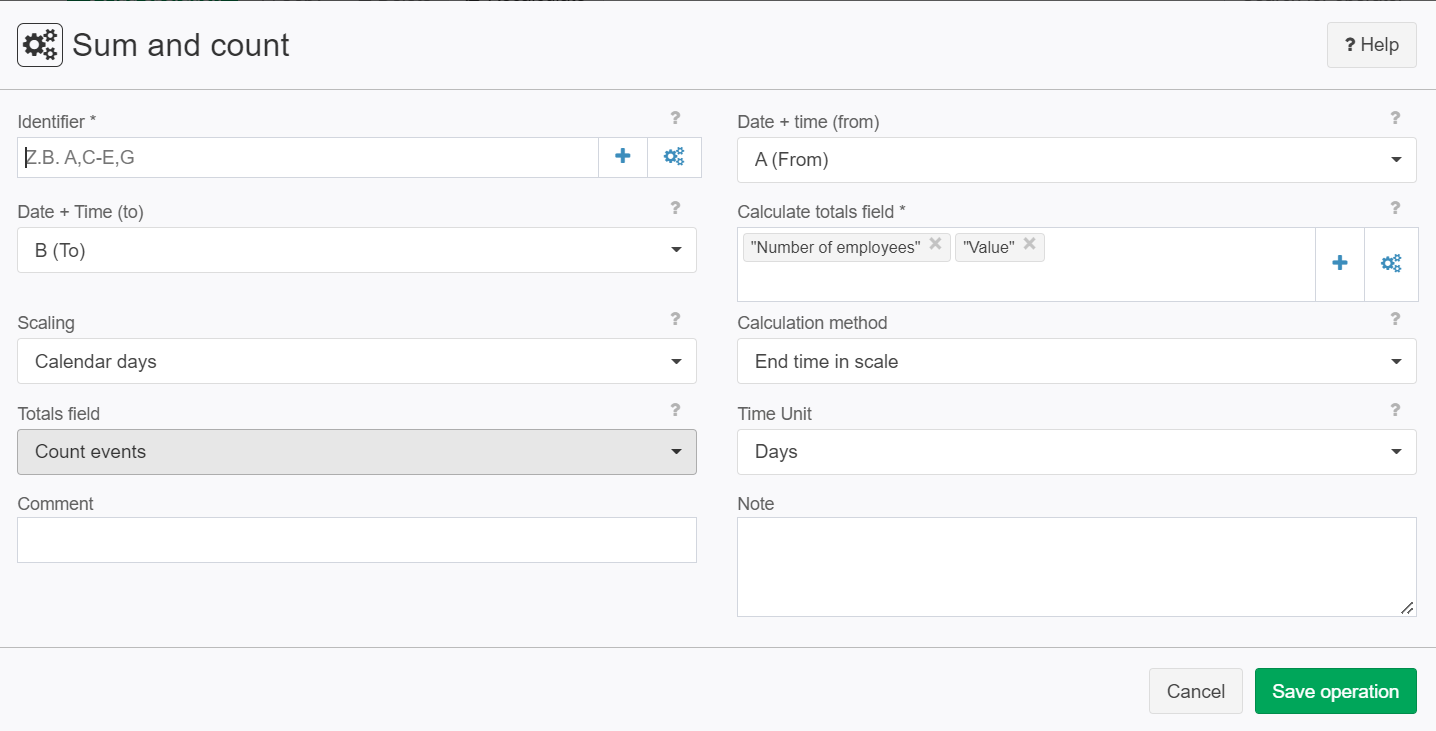
Example: Sum events
Situation | The following input record shall be analysed for the summation of events:
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Settings |
| ||||||||
Result | For Count events the setting Time unit has no influence. | ||||||||
Project File | - |
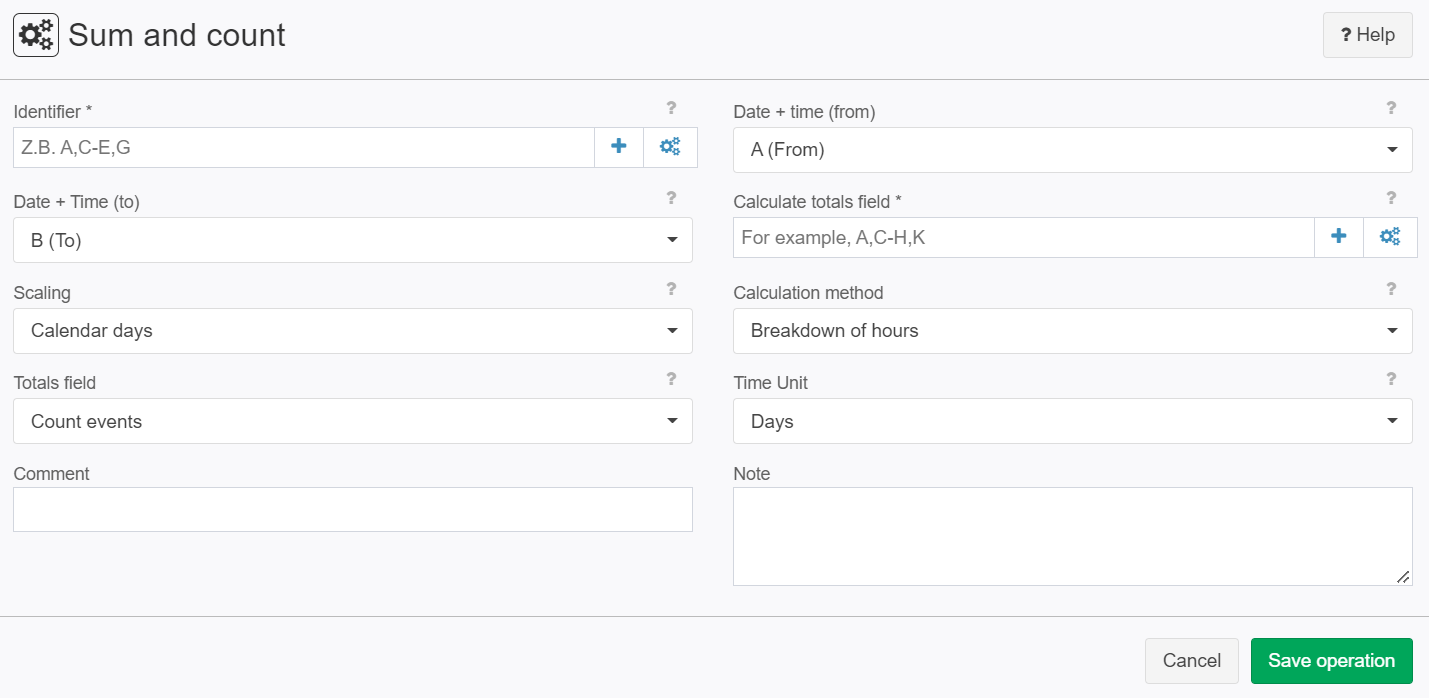
Example 4: Count events
Situation | The following input record shall be analysed for counting events:
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Settings |
| ||||||||||||
Result |
For Count events the setting Time unit has no influence. | ||||||||||||
Project File | - |
Troubleshooting
Nothing known up to now.